Food Chemistry & Natural Product Chemistry
Hideyuki Ito, PhD
Scientific Focus
Major Areas of Research
- Isolation and characterization of bioactive natural products
- Bioavailability of functional polyphenols
- Intestinal immunomodulatory effect of natural products
- Prebiotic effect of natural products
- Neurotrophic activity of polyphenols
- Interaction between food and drugs
Current Research Interests
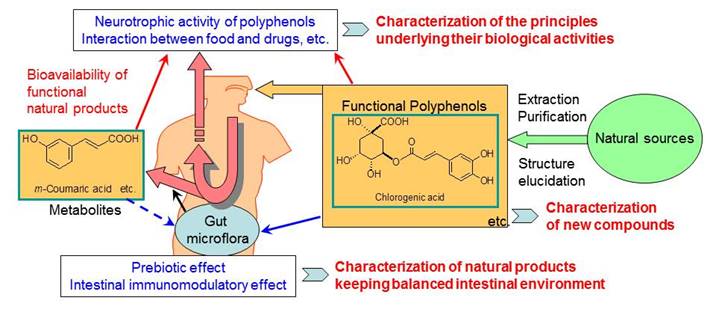
Polyphenols are phytochemicals prevalent in medicinal plants and foods, and are the major source of antioxidants in our diet. Epidemiological studies of dietary polyphenols suggest that consumption of polyphenol-rich foods and beverages may contribute to the prevention of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes. Most evaluations of the biological activities of natural products are targeted toward plant components. The bioavailability of functional polyphenols after ingestion is not fully understood.
We now focus on investigating the biological properties of dietary polyphenols including the bioavailability of functional polyphenols to characterize the principles underlying their biological activities.
Recent Research Topics
- We isolated and characterized seven urinary and gut microbial metabolites in rats after the ingestion of geraniin, which is a typical ellagitannin found in Geranium thunbergii.
- We evaluated the neurotrophic activity of dietary polyphenols using primary cultures of fetal rat hippocampal neurons in a serum-free medium. Chlorogenic acid and its metabolite m-coumaric acid were found to promote neuronal differentiation.
- We investigated excretion of polyphenols and their metabolites in human urine after consumption of cranberry juice extensively, and evaluated inhibitory effect of cranberry polyphenols and their urinary metabolites on biofilm formation of E. coli. Ferulic acid, isoferulic acid, vanillic acid, homovanillic acid, and o-, m– and p-coumaric acids, showed potent inhibitory effect on biofilm formation by E coli.
- The defense to these pathogens is initiated by secretion of immunoglobulin A (IgA) from the intestinal mucosa. Juzentaihoto and hochuekkito elicited IgA production by murine Peyer’s patch lymphocytes. A common component crude drug of these medicines, licorice, promoted IgA production.
- We systematically evaluated the inhibitory effects of 60 polyphenols and related compounds on human cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and CYP2C9 activities by in vitro assay to investigate whether some polyphenols induce drug interactions. We found that three coumarins and 12 flavonoids significantly suppressed CYP3A4 or CYP2C9 activities.
Selected Recent Publications
- Ito, H., Li, P., Koreishi, M., Nagatomo, A., Nishida, N., and Yoshida, T., Ellagitannin oligomers and a neolignan from pomegranate arils and their inhibitory effects on the formation of advanced glycation end products, Food Chem., 152, 323-330 (2014).
- Ishimoto, H., Shibata, M., Myojin, Y., Ito, H., Sugimoto, Y., Tai, A, Hatano, T., In vivo anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of ellagitannin metabolite urolithin A, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 21, 5901-5904 (2011).
- Kimura, Y., Ito, H., Ohnishi, R., and Hatano, T., Inhibitory effects of polyphenols on human cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2C9 activity, Food Chem. Toxicol., 48, 429-435 (2010).
- Ito, H., Iguchi, A., and Hatano, T., Identification of urinary and intestinal bacterial metabolites of ellagitannin geraniin in rats, J. Agric. Food Chem., 56, 393-400 (2008).
- Ito, H., Sun, X.-L., Watanabe, M., Okamoto, M. and Hatano, T., Chlorogenic acid and its metabolite m-coumaric acid evoke neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neuronal cells, Biosci. Biotech. Biochem., 72, 885-888 (2008).
